Essop Merrick produced videos giving an analysis of women’s strength training. These are mostly instructional with some exercise physiology in the content. While his knowledge is extensive, there are some elements that are critical that are missing from the videos. It is true that men and women can learn from one another when it comes to training. Method is critical when designing a training program. Also anatomical and physiological differences must be accounted for in certain approaches. Simply acknowledging differences does not constitute sexism. Essop stresses that point, but makes general statements about feminism. Not all feminists are power feminists or sameness feminist. The problem as he points out is that they think sameness equates to true equality. Everyone is different and this is not an indication of inferiority or superiority. It is not a stereotype that men are stronger than women; it is biological and physiological fact. That being understood physical fitness capacity can vary among individuals regardless of sex . There are numerous factors that determine physical strength and the video makes the mistake of saying it is primarily testosterone. Genetics, body type, body composition, and muscle fibers play essential roles. If a person is to be scientific in their analysis, one should do more research. It is not about “defining strength in a different way” or “being strong in a different way.” It it is about reaching maximal physical fitness capacity. When men and women train on the same regimen male physical fitness capacity will be higher. This does not mean women cannot reach a level that is high relative to their size and anatomical structure.
There are multiple factors that contribute to physical strength. Age does play a role in muscular strength. The best period for maximum growth is between the ages ten to 20. As a person ages their muscle mass will decrease if they do not exercise. obviously, as children grow into adults, there strength level increases due to larger body size. Puberty is the period in which males have a dramatic change in endocrinology. Testosterone levels increase causing denser bones, ligaments, tendons, and more muscle mass. Women do not get a strength spurt, rather estrogen and progesterone allow for more storage of fat.
However ,somatotype is also important. While a man may produce more testosterone a man with an ectomorphic or endomorphic body type may struggle to build muscle like a mesomorphic woman. This is independent of endocrinology and sex. Male and female muscles do not differ in terms of histology. Male and female muscles can respond to training and function in a similar manner. There is a difference in the total amount of muscle mass even with highly trained female athletes. Women have a higher body fat percentage even when reaching upper levels of muscular development. Fat does not contribute to strength generation.
Sexual dimorphism effects physical fitness capacity.
Then there is also the factor of muscle fiber type. This must be clarified before discussing muscular hypertrophy. There are different types of muscle fibers. Fast twitch muscle fibers generate more power, but have less endurance. Slow twitch fibers do not have the same level of power compared to type II fast twitch. Although the type of muscle fibers vary among sex, men on average have more type II muscle fibers compared to women’s more endurance based type I muscle fibers. If an athlete is training for pure strength, type II muscle fibers would be the most helpful. So it is possible for a woman with more type II muscle fibers to have more strength, even if a man is producing more testosterone. Strength and power training is the most effective method for recruiting the most muscle fibers for strength.


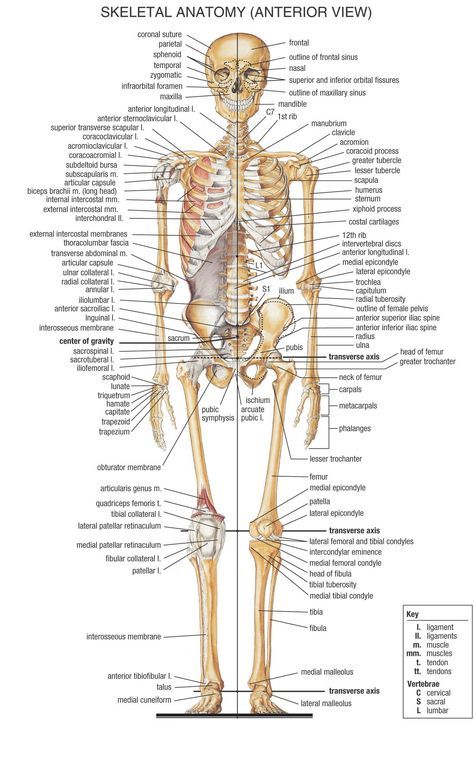
The skeleton also is a factor.Bone density is higher in men. The skeleton acts as a support system for organs and houses muscles connected by ligaments and tendons.Limb length also can aid strength. People with shorter limbs can have an advantage in lifting due to leverage factors. Longer limbs mean more space for muscle compared to shorter limbs. Tendons can provide biomechanical advantage relative to point of tendon insertion. There also remains a difference in upper and lower body strength between men and women partially influenced by skeletal structure. Men have broader shoulders, which means that there is more area for muscle. A woman can build significant strength in the upper body, but smaller shoulder width and size would not allow for muscular levels of the male upper body. Men have an estimated 50% greater upper body strength. There is even a strength difference in the lower body estimated at 30%. Women are closer to men in the lower body.
Genetics and the function of the nervous system also have major roles to play in physical strength. There have been genes that have been identified associated with strength. These genes include PEX14, ACTG1, TGFA, and SRYT1. These genes are responsible for muscle fiber function and the nervous system communication between them. Women are also the carriers of these genes. There are most likely more genes that contribute to muscular strength. The MSTN gene provides directions to myostatin a protein responsible for regulating muscular growth. If an a person has low myostatin levels, then building muscle would be easier. These factors are independent of biological sex and endocrinology. Sexual dimorphism can be flexible in this regard. Neural adaptation is also important to strength. If the motor cortex can be trained to efficiently recruit muscle fibers, this means the body can reach a certain strength potential. The motor neurons are classified as efferent neurons which working through the spinal cord produces muscle contraction producing proprioceptive sensitivity. The nervous system has to be included in this discussion of strength.

Neuromuscular efficiency has to be considered when making strength assessments. This explains why someone who appears to be bigger may not be as strong as someone who has trained differently. Testosterone is a major help in protein synthesis, which allows for more hypertrophy. Yet.it is not the sole factor in physical strength.
Strength depends on which training method is used and the type of muscular hypertrophy it causes. Exercise increases physical fitness levels. There are no women’s exercises or men’s exercises. If the muscular and skeletal system are similar in terms of physiology any exercise should work to produce stimuli.
Even using the term “women’s strength training” seems somewhat inaccurate. Strength training is strength training no matter what a person’s sex is. The major factors related to it come down to sarcoplasmic and myofibular hypertrophy. The video gives a general explanation of both. Myofibular hypertrophy requires high intensity, low reps, and medium sets. Myofibrils are formed from bundles of myofilaments. Each muscle cell contains these myofibrils and they are responsive to load stimulus. This means micro-trauma must be applied to the individual fibers inducing repair during a recovery period. Overload must be maintained to see muscular hypertrophy occur. Sarcoplasmic hypertrophy involves medium intensity, higher reps and sets. Sarcoplasm is the energy sources that encase the myofibirls. This includes ATP, glycogen, creatine phosphate, and water. This involves scaroplasmic expansion. The problem is that it would be premature to say which type of hypertrophy favors women. Other factors involved in strength must be realized when considering this.

It may appear that sarcoplasmic hypertrophy favors women more in terms of the disparity in intensity, but there has never been an experimental basis for this. This question relates to whether or not women should train like men or try another method. The best answer is designing a program specific to a person’s unique physiology. There are women who are at various fitness levels and will see more results compared to others. While some methods are not interchangeable with men and women it can apply to various individuals regardless of sex.
There is a difference is total absolute strength gains. The chart that was made for the presentation gives a least an general estimation of physical capabilities. However there has to be a level of precision. Weightlifting records show the the total aggregate of fitness capacity. Crossfit records also provide a more accurate assessment. Weight and height add an advantage. The performance range differs between novice lifters and advanced ones.


Strength level wise women can reach the level of an untrained male. Their strength could be slightly more than an untrained male given the trained woman’s size and total weight. This also depends on training method. If a woman only does cardiovascular exercise, this will not dramatically increase physical strength. The act of getting strong is not sexist. The process from going from weak to strong is the increase in fitness. As data shows, women can improve their performance like men if they train, consume the proper diet, and focus on periods of recovery. The major challenge is that for women it is a trial and error method, because very few exercise physiology studies focus on women. The majority of these studies are conducted on men. This causes confusion about how women should best train for maximum performance. Also interpretation of data is important. These are totals of each athletes’ performance. This could mean that there may be a level of overlap in performance when comparing individual male and female athletes. Women’s athletic performance should not be considered as poor, rather a representation of weight class. Weight class was designed to give smaller people and extremely large people opportunities to compete in sports on an equal basis. Seeing as women are smaller their performance is a representation of their weight class. No one ever says that smaller male athletes are inferior. They are admired for their skill, yet women do not get such accolades.
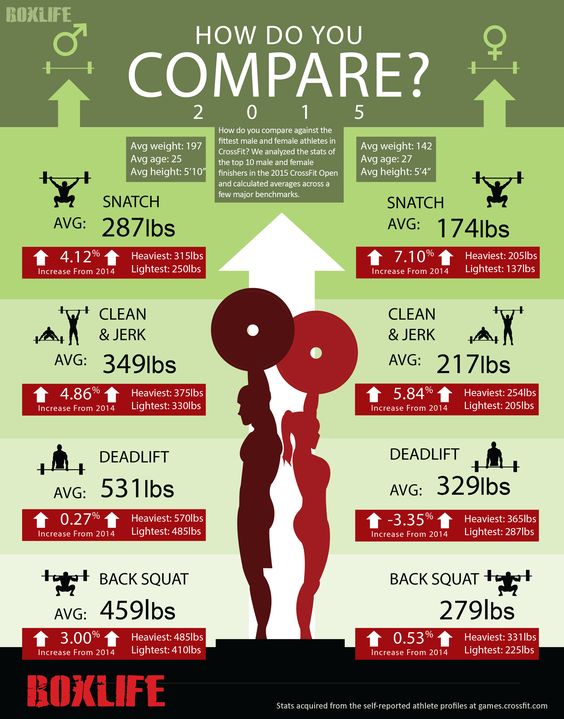


Women can improve their performance, but they have a harder time reaching higher fitness levels. Less muscle means more work has to be done. The difference in metabolism means that women have to be careful with the diet. Activity level most be high enough so that food does not metabolize into fat. Calorie intake needs to be the right amount to provide energy and feed the growing muscles. It is not just biology that influences athletic performance; there are sociological factors.
There has been for a longtime sexism in sports. The problems does not stem from ignoring the differences or “celebrating the good in one of the groups.” Discrimination stems from bias and prejudice as well as the conviction that certain groups do not deserve the same rights or opportunities. Such thought believes that certain groups should not have access even to the same leisure activities. The reason so few women are present in serious strength training gyms is because they have been excluded in the past. Although women’s numbers have increased in sports it still is below the participation level of males. Cultural standards of beauty and restriction to training facilities kept many women out of sports. The passage of Title IX changed this allowing girls in school the opportunity to play sports. From 1972 onward there would be a dramatic increase in female athletic participation. This a demonstration of how public policy can change a social ill if implemented correctly.

There are many who want to reverse such changes. Claims of “reverse discrimination” or attempts to bring down other groups of another are made by conservatives. This is nothing more than an attempt to reimpose the old order. It is too late to keep women out of sports, but there are numerous attempts to undermine it. Limited television broadcast, lack of sponsorship, or sex discrimination are the most notable methods. Gender verification tests, no competitive venues, and public ostracism made it difficult for women to compete professionally in sport. When the modern day Olympics came into existence in 1896, it was a male only event. Although women participated in sports since the ancient world 19th century cultural sensibilities rejected the idea of a physically strong woman.
 It was not until 1991 that the IOC ruled that any new sport introduced to the games had to include women. Despite these gains, women around the world do not have the same opportunity for athletic competition. Women may be faced with extreme poverty, lack of reproductive rights, or limited education. If a ruling group does not want to share power and continues to oppress, then it must be taken down. So far, certain institutional structures have changed for the better for women competitors. Considering the past women’s advancement in sport is impressive. These obstacles demonstrate why many are still trying to catch up in the sports world.
It was not until 1991 that the IOC ruled that any new sport introduced to the games had to include women. Despite these gains, women around the world do not have the same opportunity for athletic competition. Women may be faced with extreme poverty, lack of reproductive rights, or limited education. If a ruling group does not want to share power and continues to oppress, then it must be taken down. So far, certain institutional structures have changed for the better for women competitors. Considering the past women’s advancement in sport is impressive. These obstacles demonstrate why many are still trying to catch up in the sports world.
Exercise does not differ between men and women. There are no “girl exercises” or “men’s exercises.” This can be described best with the squat and the deadlift. Essop articulates it as a movement pattern. Training with correct form and avoiding injury can create a safe as well as effective workout. The notion that strength and physical prowess was a male only attribute has created a bias against women. The frailty myth was created by 19th century pseudoscience with the conviction that the female body was biologically inferior. Many thought that if women became too strong this would harm their ability to become pregnant. This was proven false in the 20th century and women began to enter the world of sports and fitness.
Strength training is strength training no matter who does it. So saying there is a “women’s strength training” makes no sense. Exercise like the deadlift or squat can best be seen as a movement pattern. Men can even learn many techniques from women in terms of lower body strength training. Women have an advantage in terms of deep squats because of their pelvic structure. Knowing differences between the sexes allows for a more efficient training program that can meet an athletes needs. Intensity and volume can be inversely proportional. That means the heavier the weight, the less time one can lift it. The lighter the weight the more time you have to lift it. Volume can either be adjusted to promote growth or more physical strength. This can to an extent be fluid rather than a set quantitative value. There may be a way theoretically to reconcile the difference in maximal strength between men and women Essop suggests. The approach may be by increasing volume. Splitting such a task into sets reduces the labor or possible strain. This may counter the intensity by equalizing the workload. The variety of exercise can also effect performance outcomes. Women’s looser joints and flexibility also provide an advantage in particular ranges of motion. Squat, bend, and lunge are the movement patterns for the hips.
There are also three planes of movement which include frontal, transverse, and sagittal. Other exercises also involved in the movement pattern include step ups and hyper extensions. Variety when done will challenge the muscle and allow for significant increase in total amount of weight lifted. There is the question about whether free weights or machines are better. To date there has not been a conclusive study to prove which one is better. The conjecture is that both are best to use, but there is no official verification of that. Women’s recovery from training gives them a benefit, which men do not have. While male absolute strength allows for more intensity, this means recovery periods would be longer. Doing high intensity workouts in such a manner also increases the risk of injury. Women can build immense core strength if they understand that the nervous system is stimulated by the activation by that section of the body. It is not by isolation.

Using this particular approach can help athletes avoid over training. This still does not eliminate the absolute strength difference between men and women on a similar program. Sexual dimorphism is flexible in particular aspects. Core strength demonstrates through training that some elements one show a small physical performance difference. Elite men and women it is bigger in absolute strength. Becca Swanson is stronger than many men, but would not be stronger than the strongest man.
Her range of strength would even surpass trained males. What can be extrapolated from this information is that being female does not limit athletic potential. Women are neophytes to the professional sports world and developing training programs is an experimental process. There are numerous training programs and fitness advisory websites, but this can be confusing to a person just starting. There has to be a framework to follow for success.
Essop reduces the process of strength training regimen to certain steps. The first step requires stimulating the muscles. That would be the exercising process that follows after that . This follows recovery allowing the body to repair and get ready for the next training period. Super compensation is the diet and rest in total. This should be repeated and be consistent.
Essop’s view is that it should be retrospective in function rather that a set schedule. The problem with being set on one exercise, then correct form, and then progressive overload. This may not work for everyone and may just be too restrictive. The objective should be to enhance the body through variety and challenge it. The standard operation of the personal trainer system may be too limited for higher physical fitness targets. The problem is being too focused on one exercise. The emphasis should not be the form its self rather the movement pattern and its particular features. The squat can have the neutral neck, thoracic extension, as well as external rotation of the hands and feet. The femurs of the body will be going back and the hips will be lateral during the hip hinge.
Generally, Essop calls this women’s workload training. It involves several steps. The first step involves selecting a movement pattern. This can either be the squat, lunge, or bend. The second part involves either the two foot, one foot, or split stance. Then comes the question of adding weight loads and which part of the body should this be done to. Starting off one should learn the basic patterns. When the basics are mastered, then one can move on to more advanced movements. This can result in simple training progression. Having higher range in motion can lead to more activation of muscles with less weight. This will result in muscular hypertrophy just the same as lifting heavy. The only difference may be is that this method would be less strenuous and efficient compared to a longer training program. There are simple exercises that one must remember that exist on a spectrum. These include the bend, squats, and, lunges. These exercises are dependent on which joint is moved first and ultimately effect total activation. The exercises as the video argues is that it functions on a spectrum. The movements are part of this spectrum and doing them a specific way in a rigid fashion may not be the best approach. Having correct form can prevent injury, but it should be understood that exercises are more similar than previously thought. Essop makes cogent arguments, but it must be realized women still need to be studied more in terms of exercise physiology. It cannot be stated with complete certainty what is the full extent of women’s physical fitness capacity.

























Reblogged this on Mike Row Wang.
LikeLike